Real-Time vs Historical Alternative Data: Investment Impact
Alternative data provides insights from non-traditional sources like social media, satellite images, or IoT devices. This data helps investors spot trends and make informed decisions. But should you focus on real-time data or historical data? Here's a quick breakdown:
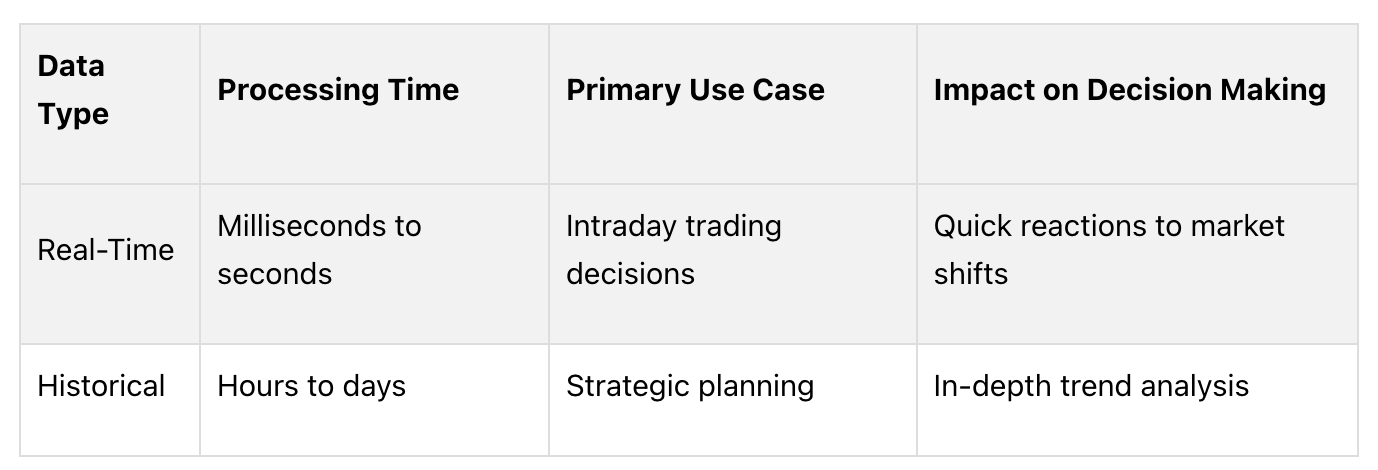
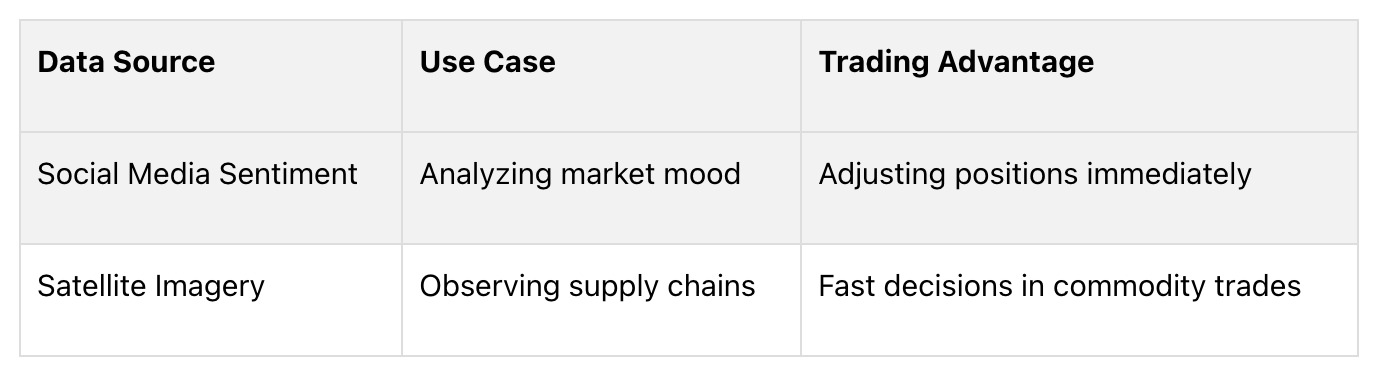
Real-Time Data: Best for fast decisions like day trading. Examples include live social media sentiment or satellite imagery of supply chains.
Historical Data: Ideal for long-term strategies, backtesting, and trend analysis. Examples include years of past consumer behavior or market performance.
Quick Comparison
Key Takeaway: Combining real-time and historical data offers a balanced approach - quick responses grounded in long-term insights. Hedge funds and institutional investors increasingly use both for smarter strategies.
Differences Between Real-Time and Historical Alternative Data
Time-Based Differences: Current vs Past Insights
Real-time alternative data delivers updates as events happen, offering immediate market information. For example, satellite imagery can monitor shipping activities at key ports in real time, providing quick insights into supply chain operations. On the other hand, historical data focuses on past market activities, helping investors analyze long-term patterns and trends. These differences in timing shape how each data type supports various investment approaches.
Speed and Timeliness: The Role of Immediate Data
The speed of real-time data makes it ideal for intraday trading, where fast decisions are crucial. Meanwhile, historical data is better suited for developing long-term strategies. Here's a quick comparison:
"Alternative data sources can give investors a critical edge in their investment strategies – particularly when macroeconomic insights can be delivered in real-time using AI and powerful data analytics techniques." [1]
While speed is a major advantage of real-time data, the ability to handle and store information efficiently is just as important for transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Data Volume and Storage: Processing and Storage Challenges
Historical data requires significant storage capacity and robust systems to manage its large datasets. Real-time data, on the other hand, depends on high-speed systems to minimize delays. Platforms that combine both real-time and historical data are now essential for ensuring data accuracy and accessibility. Investors who can skillfully handle both types of data gain an advantage by blending instant responsiveness with a deeper historical perspective [3].
What is Alternative Data? Origins, Applications, and Investment Impact
Using Real-Time and Historical Alternative Data in Practice
Knowing how to use both real-time and historical data effectively helps investors create strategies that balance quick decision-making with a deeper understanding of long-term trends.
Real-Time Data: Immediate Market Applications
Real-time alternative data has changed the game for high-frequency trading and market-making. Traders now use tools like social media sentiment analysis and satellite imagery to gain quick insights and act fast. Platforms analyzing TikTok, Reddit, and YouTube trends allow traders to spot shifts in sentiment as they happen.
Investment firms also rely on real-time data to monitor supply chains and make rapid trading decisions. For instance, tracking real-time web traffic can help predict earnings announcements or shifts in consumer behavior.
While real-time data is great for reacting to immediate changes, historical data provides the context needed for deeper, more strategic insights.
Historical Data: Building Long-Term Strategies
Historical alternative data is key for crafting investment strategies that last. By analyzing years of past performance, investors can backtest strategies and assess risks with more confidence.
For example, historical web traffic or social media trends can be used to build predictive models. These models help forecast market movements and uncover new investment opportunities.
Some common uses of historical data include:
Backtesting strategies across different market conditions
Studying consumer behavior and market correlations over time
Developing models to evaluate and manage risks
Turning raw data into useful insights remains a challenge [3]. Leading firms tackle this by using strong data management systems and standardized processes that work seamlessly with both real-time and historical data.
Discover Alternative Data Insights
Access comprehensive consumer data, track market trends, and gain actionable insights with TickerTrends' innovative data terminal and API services.
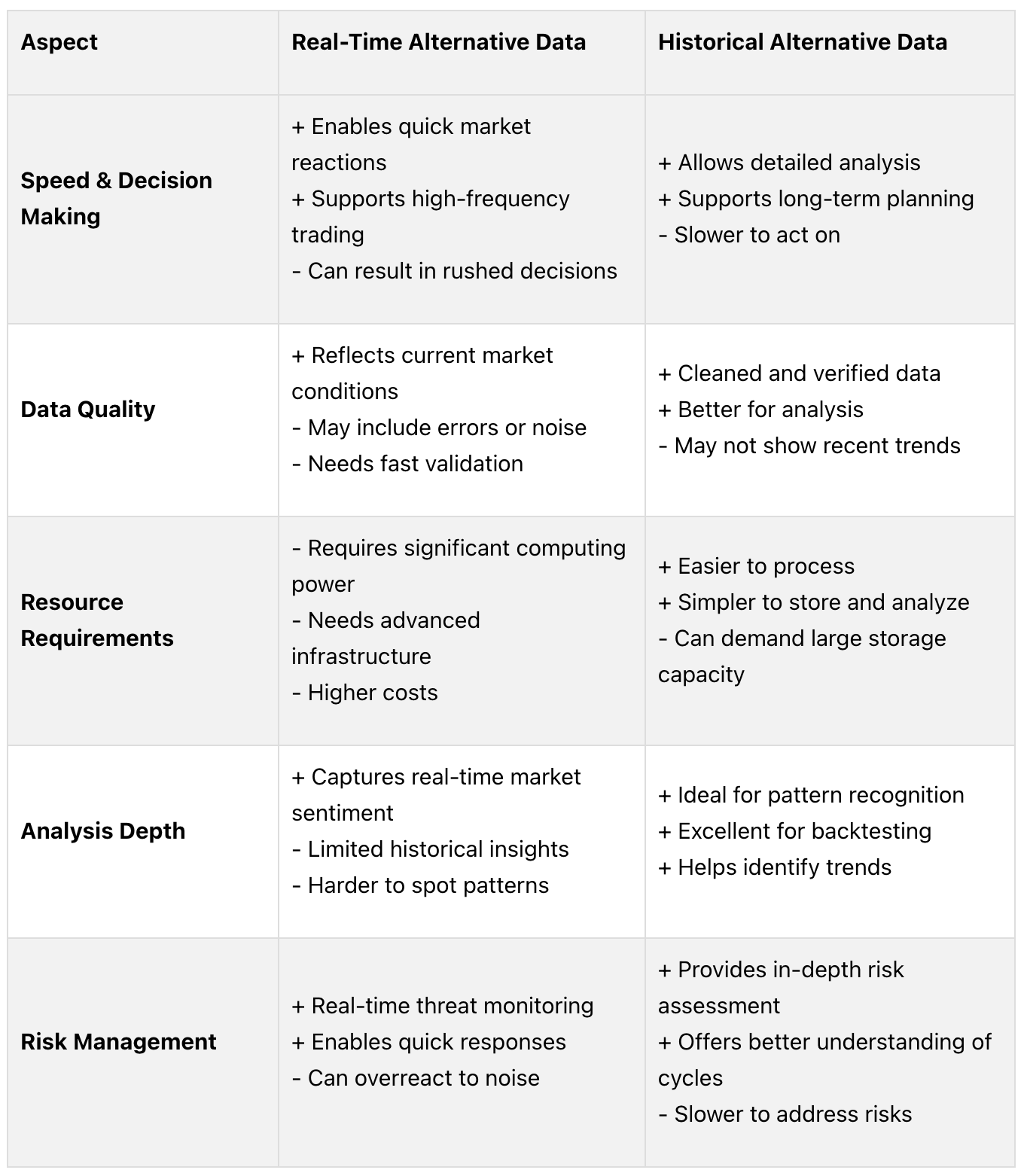
Pros and Cons of Real-Time vs Historical Data
Knowing the strengths and weaknesses of real-time and historical alternative data helps investors decide which type aligns with their goals. Both serve different purposes and come with their own advantages and challenges.
Pros and Cons Comparison Table
Real-time data is perfect for fast-moving markets but can lead to decision fatigue if not managed carefully. On the other hand, historical data supports in-depth strategies but requires more time to process. The choice depends on the investor’s strategy and time horizon.
Many institutional investors combine both types for a well-rounded view of the market. For instance, hedge funds might analyze real-time social media trends to adjust positions quickly while using historical data to fine-tune their broader strategies.
Combining Real-Time and Historical Data for Investment
Integrating Data Types for Market Analysis
Bringing together real-time and historical data allows investors to balance immediate market signals with long-term trends. This combination helps reduce the noise often found in real-time data and adds timely relevance to historical insights. The goal? To make smarter, more informed decisions.
Financial institutions use this approach to identify short-term opportunities while grounding them in historical context. For example, a sudden spike in social media sentiment can be cross-checked against past trends to determine whether it's a genuine signal or just market noise.
Here’s how to structure the process:
Data Collection: Gather real-time feeds from sources like social media, web traffic, and app usage alongside cleaned historical datasets.
Signal Validation: Compare current market signals with historical data to uncover meaningful patterns.
Risk Assessment: Use both data types to evaluate potential risks and refine strategies.
Modern tools make it easier to integrate these workflows, offering seamless access to multiple data streams.
Tools for Data Integration
Platforms designed for data integration simplify the process of combining real-time and historical insights. One example is TickerTrends, which provides access to real-time social media data and historical trends from platforms like TikTok, Reddit, Google Search, and YouTube.
The best tools for this purpose should include features like:
Additional capabilities like standardized formats ensure compatibility between datasets, while automated data validation minimizes errors. Tools with flexible query options allow users to analyze data across different timeframes, enabling a more precise and strategy-driven approach.
Conclusion: Selecting Data for Investment Goals
When combining real-time and historical data, it's crucial to align these insights with specific investment objectives.
Key Takeaways
Choosing between real-time and historical alternative data - or using both - can strongly influence investment results. The key is to match the type of data with your investment goals and the current market environment.
"Incorporating alternative data generally involves a long-term commitment of resources as the journey from data discovery to full integration is typically spread across multiple years" [3]
This long-term view underscores the importance of a well-thought-out strategy when integrating data into investment processes.
Different investment goals require distinct data strategies. Here's how they align with real-time and historical data:
Quality sources, robust infrastructure, and regular evaluations are essential for effective data integration. In financial markets, alternative data usage is growing, with hedge funds and institutional investors increasingly relying on sources like mobile app data and satellite imagery to stay ahead [2].
FAQs
What alternative data do hedge funds use?
Hedge funds like Point72 and Two Sigma have transformed investment strategies by tapping into alternative data. Let’s break down the key datasets and how they’re used:
By combining real-time data (like social sentiment) with historical trends, hedge funds refine their strategies and reduce risks. A notable example: tracking corporate jets during the Occidental Petroleum-Anadarko deal helped predict M&A activities early [4].
Renaissance Technologies offers another example by blending web-crawled data with traditional market insights, showing how alternative data boosts quantitative trading strategies.
When choosing alternative data sources, hedge funds focus on these factors:
Data quality and consistency: Reliable and accurate data is a must.
Integration with existing systems: Smooth compatibility ensures efficiency.
Balancing costs and returns: The expense should justify the potential gains.
Regulatory compliance: Adhering to privacy laws and regulations is critical.
This approach gives hedge funds a sharper edge in a competitive market.